Preface
- The anti-aging industry is a multi-billion dollar fertile ground for cons and scams, with some being subject of Senate and congressional inquiries.
- Scientific breakthroughs exploited by the sensationalist press have been long opportunistically repackaged by profiteers. This "scienceploitation" is evident in stem cell clinics - using the language of science to give a veneer of legitimacy to their unproven therapies.
- Scientific journals remain the gold standard for establishing the best approximation of truth about our shared reality. Peer-reviewed medical literature is the worst way to establish facts about our health, except for all the others.
- Because old age is the greatest factor for most of our diseases, the leading cause of death is actually aging. High cholesterol can increase your risk of heart disease, but an 80 year old has even a higher magnitude of risk than a 20 year old.
- Instead of focusing on individual diseases, decelerating aging could address the leading killers as well as other impairments.
- Is aging itself a disease? In the past many things like masturbation or homosexuality were considered diseases. If aging was classified as a disease, more resources would be allocated to it, similar to obesity in recent times.
- Studies show that we're living longer, but we're living sicker. Healthspan is the period of life spent in good health, free from chronic disease and disability.
Introduction
- This book is not about immortality but rather how to age with grace and vitality rather than suffering from the ravages of infirmity and decrepitude.
- As old as the Epic of Gilgamesh (4000 years ago) humans have been searching for the elixir of life that will cure aging. Evolution has produced lifespan in animals that vary, from mayflies whose lives last a few minutes to clams over 500 years. The immortal jellyfish apparently do not age and could technically live forever.
- There is much skepticism in the scientific community where many believe aging is an irreversible process. However, there is hope in that some genetic and dietary manipulations yield an increase in lifespan of some species in the laboratory.
- There are 4 parts to the book:
- 11 most promising pathways for slowing the sands of time, with proposals for targeting them with diet and lifestyle changes.
- Behaviours of those in the 5 longevity hot spot "blue zones" around the world share in common. Best and worst foods and beverages. The "longevity vitamin" ergotheioneine, and the best exercise and sleep routine for the longest healthiest life.
- Preserving the functions of bones, bowels, circulation, hair, hearing, hormone balance, immune function, joint health, mind, muscles, sex life, skin, teeth, vision, and your dignity in death.
- Specific foods, supplements, or behaviours that have the potential to offer the best opportunities to slow aging or improve longevity.
Slowing 11 Pathways of Aging
Introduction
- Studies on identical twins and fraternal twins show that about 15 to 30% of our lifespan is determined by our genes, which means how we live our lives may determine the bulk of our destiny.
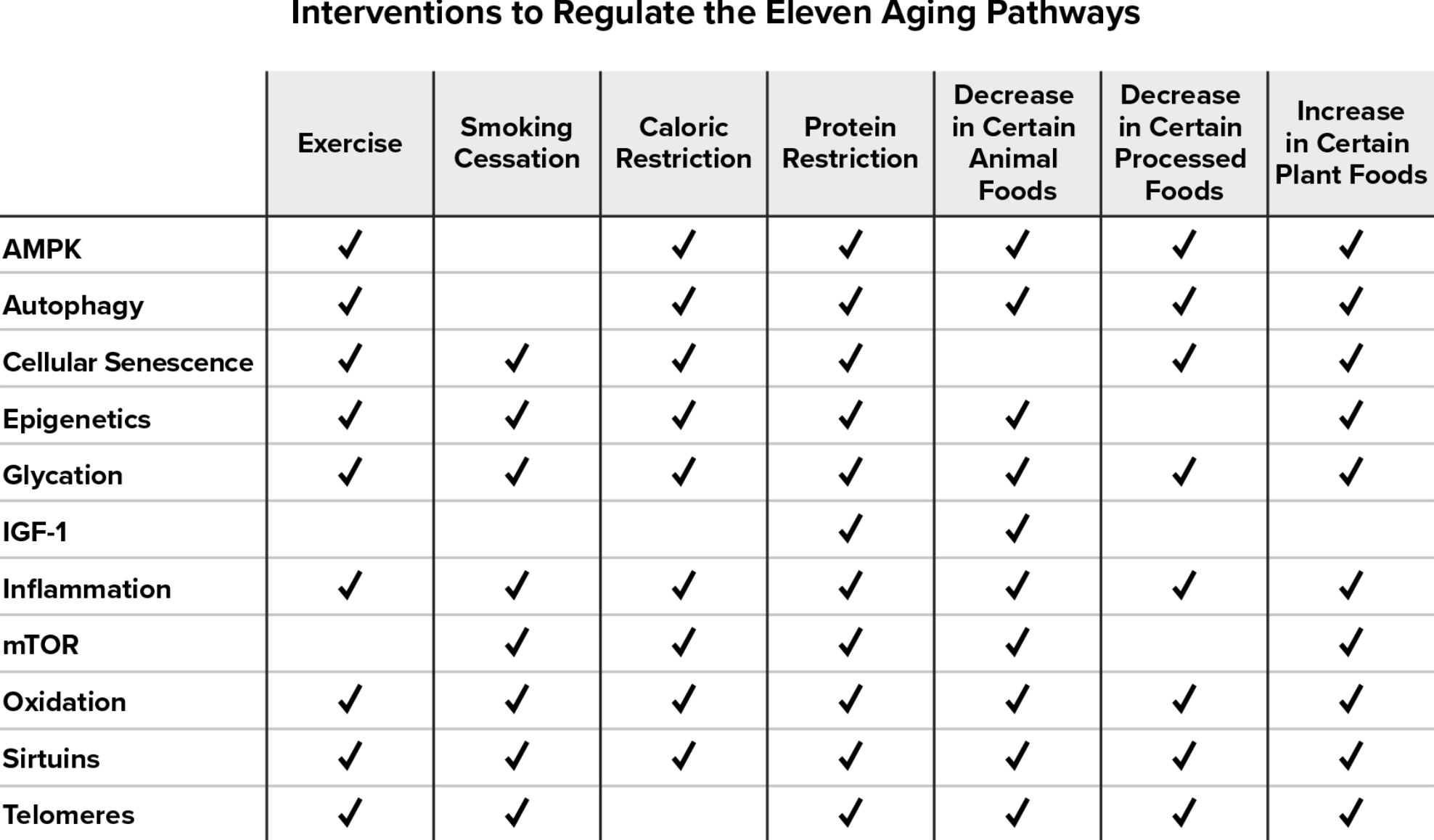
- The abused term "anti-aging" should be reserved for things that can delay or reverse aging through the targeting of one or more of the established aging mechanisms.
AMPK
- AMP-activated protein kinase is an enzyme that acts as a sensor for plants and animals, similar to a fuel gauge in a car. AMPK plays a role in storing fat to burning it to restore energy.
- Autophagy is a process in which defective cellular components, such as misfolded proteins are broken down and scrapped for spare parts. AMPK induces autophagy, which institutes a sort of cellular reset.
- There are 3 ways to establish an aging pathway:
- Does the factor worsen with age?
- If you amplify it does it accelerate aging?
- If you dampen it, does it slow aging and extend lifespan?
- Since AMPK is activated by a fuel shortage, if we don't want to limit the energy going in through our mouths then we have to ramp up the amount of energy going out through our muscles. This is why AMPK activity can be detected through exercise, which can result in weight loss.
- AMPK activation can also lead to mitochondrial biogenesis, formation of extra mitochondria, the power plants where fat is burned. Old mitochondria are discarded and new ones are built through mitophagy.
- The drug metformin can treat type 2 diabetes by boosting AMPK, but on healthy individuals it does not appear to have the same effect.
- Saturated fat called palmitic acid suppresses AMPK, most concentrated in meat and dairy fat. Consumption of these products are a leading cause for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Foods to increase AMPK:
- Legumes and whole grains
- 2 teaspoons of barberries
- Dash of ground black cumin
- Hibiscus tea with lemon verbena
- 2 teaspoons of vinegar (never taken straight, on food or dilute in tea)
Autophagy
- When food is scarce, cell division slows down and the process of autophagy starts - our body starts rummaging through our cells in a salvage operation looking for anything we don't need (defective proteins, malfunctioning mitochondria, etc) and upcycles it, turning it into fuel or new building materials, thereby renewing our cells. Autophagy plays two major roles: nutrient recovery and quality control.
- In the modern context, easy access to food means our baseline rate of autophagy is low and gets lower as we get older. This can lead to more accumulation of cellular debris, which can further impair our aging cells.
- 60 minutes or more of moderate to vigorous aerobic exercise can induce autophagy, high-intensity interval training and resistance exercise didn't seem to make a difference.
- The enzyme mTOR deactivates autophagy - animal proteins activates mTOR which may also suppress the autophagy process.
- Carbohydrate-rich foods like french fries and potato chips contain acrylamide which is a chemical formed when carbohydrates are exposed to high temperatures. Acrylamide can inhibit autophagy.
- Coffee, as well as decaf, was associated with a range of health benefits. The polyphenol chlorogenic acid is the most abundant antioxidant in coffee beans, which is linked to longevity.
- Instant coffee doesn't seem to affect chlorogenic acid levels, but brewed coffee has higher chlorogenic acid content than espresso. Also, those drinking paper-filtered coffee had lower mortality rates than those drinking unfiltered coffee. This is due to the cafestol present in the fine particles in the coffee.
- Spermidine plays a key role in regulating cell growth. Our cells make it from arginine (amino acid), some bacteria in our gut produce it, or we can get it from our diet.
- Studies show high spermidine intake was associated with a lower risk of all major causes of death. The difference in death rate was as if those eating more spermidine were 6 years younger.
- Highest foods containing spermidine per serving are: tempeh, mushrooms, natto, mangoes, and soy milk. Wheat germ has the smallest serving size (one tablespoon) and is the cheapest source of spermidine.
- Boosting autophagy:
- 60 minutes of moderate to vigorous aerobic activity
- Minimising intake of french fries and potato chips
- Consume at least 20mg of spermidine everyday by incorporating foods such as tempeh, mushrooms, peas, and wheat germ
- Drinking 3 cups of decaffeinated coffee
- Increase AMPK
- Suppress mTOR
Cellular Senscence
- Hayflick demonstrated that human cells grow and divide about 50 times before entering an irreversible state of arrested replication. This helps protect the body against cancer by blocking the proliferation of damaged cells.
- It turns out nondividing cells actively damage surrounding tissues, earning them the monker "zombie cells." When our cells reach their limit and ready to retire they are programmed to release inflammatory chemicals called senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). As we age more and more senescent cells pile up the same time our immune systems start to decline. This turns into chronic systemic inflammation that characterises aging and disease.
- Quercetin, a flavinoid found in onions, kale, and apples, was shown to reduce cellular senescence.
- Fisetin, another flavinoid was shown to have senolytic properties. It is concentrated the most in strawberries.
- Piperlongumine is another senolytic compound found in pippali or long pepper.
- To slow cellular sensecence:
- Consume quercetin-rich foods, beverages, and seasonings, such as onions, apples, kale, tea, and salt-free capers
- Eat fresh, frozen, or freeze-dried strawberries
- Seasoning meals with pippali (long pepper)
Epigenetics
- Female eggs must undergo reversal of aging, otherwise eggs in women's ovaries would be millions of years old.
- In 1996 Dolly the sheep was born. The nucleus of an unfertilised egg was removed and in its place, the nucleus of an udder cell was inserted. Then, with an electric shock, the cell started dividing, no sperm required. Dolly, the first animal cloned from an adult cell, was born.
- Mice have been cloned from clones, showing that adult cells can be dialled to an embryonic state and also be rejuvenated by having any traces of aging wiped clean.
- Epigenetics meaning "above genetics," layers an extra level of information on top of the DNA sequence which is about 750 mb of data encoding 50,000 genes. All our dividing cells are genetically identical, carrying a full complement of our DNA, but each cell doesn't need to express all our genes. Epigenetics is what switches genes on and off.
- No matter our family history, the lifestyle choices we make can effectively turn on and off some of our genes.
- There are certain sites on our genome that when measuring the methylation pattern, we can predict their chronological age, surpassing telomere length. Epigenetic clocks like this can also predict your remaining life expectancy, as well as healthspan indicators such as cognitive decline, frailty, arthritis, and the progression of diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
- Epigenetic clock analyses show that women age more slowly than men.
- The first major randomised trial of calorie restriction in humans showed that dietary restriction group achieved slower age rate with 12% calorie restriction - skipping one donut a day.
- Yamanaka factors are DNA-binding proteins responsible for returning a cell to factory settings. Scientists were able to reset methylation marks with Yamanaka factor manipulation, restoring vision in old mice and rejuvenating human neurons in a petri dish.
- Methylation differences in vegans compared to omnivores is hypomethylation (less methylation) of a tumour suppressor gene and a gene that encodes a DNA repair enzyme. Since methylation silences genes, unmuzzling them may account for the lower overall cancer rates.
- Folic acid is a nutrition factor widely studied for its epigenetic effects. Natural sources of folate, like beans and greens may be best, rather than taking supplements of folic acid.
- To help slow the epigenetic clock:
- Restricting calories by 12%, which would be cutting about 250 calories out of a 2000 calorie diet (skipping a piece of pie or cake every day)
- Meeting the 400 µg recommended daily allowance of folate, which could be achieved with about a cup of cooked lentils or edamame, 1.5 cups of cooked spinach or asparagus, or 2.5 cups of broccoli
Glycation
- Maillard reaction is what gives food their distinctive brown look. It is when proteins become irreversibly glyacated, or bonded with sugar. The same reaction can occur at body temperature, leading to an accumulation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which is one of the main factors contributing to the aging process.
- As AGEs accumulate in our bones, joints, and muscles, they may contribute to osteoporosis, arthritis, and muscle weakening. Over 5-6 decades, AGE levels in our tissues double. This is not only seen as a marker for aging but an active driver of the aging process. Across the animal kingdom, the slower the rate of AGE formation, the longer species tend to live. The burden of AGEs in our tissues appears to be less of how much we make and more a matter of how many AGEs we eat.
- When muscle cells are exposed to high temperatures, they rupture and spill highly reactive amino acids that combine with blood and body sugars to form AGEs.
- Studies show that dietary AGEs contribute more to the toxic pool of AGEs in our body than our own endogenous production.
- High-fat and protein-rich foods created more AGEs than starchy and sugary high-carbohydrate foods. Sugars can look, smell, and taste similar to products of the Maillard reaction, but that's the result of caramelisation. By definition, Maillard reaction AGEs are created only when amino acids from proteins are involved.
- High-glycemic foods spike our blood sugars: cereals, dates, white rice, white potato, raisins.
- Low glycemic foods are: legumes (beans, chickpeas, split peas, and lentils), fruits, and intact whole grains.
- Lentils can benefit your metabolism hours after consumption, by feeding the good gut flora.
- Ketogenic diets are high in methylglyoxal, an inflammatory metabolic toxin that forms at high blood sugar levels. Methylglyoxal is the signle most potent creator of AGEs.
- When people were randomised to drink beverages sweetend with aspartame, monk fruit, or stevia instead of sugar, they were all found to be equally bad when it came to calorie intake, blood sugars, or insulin spikes throughout the day. Similar results were found for Splenda.
- Same foods in different forms can have different effects. Steel-cut oats have a lower glycemic index than instant oatmeal. Breads made from sprouted grains with added cracked wheat, whole wheatberries, or rye berries, or stone-ground flour are preferrable. Freezing and defrosting white bread will lower the blood sugar response.
- When starch is cooked then cooled, some of it crystallises into "resistant" starch, that is resistant to being broken down into sugars by the enzymes in our digestive tract which lowers glycemic impact. That's why pasta salad can be more healthful than hot pasta, and potato salad better than a baked potato. Sorghum and millet inherently contain resistant starch, resulting 20-25% lower blood sugar response compared to rice, wheat, or corn.
- To reduce absorption of AGEs:
- Eating an "AGE Less" diet by emphasising lower AGE foods, such as fruits and vegetables
- Cooking high-protein foods in low heat and high humidity methods, such as boiling or steaming rather than broiling or frying
- Favouring raw nuts and seeds over roasted or toasted
- Choosing lower glycemic load foods
IGF-1
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) is a growth hormone structurally similar to insulin. Interference with the signalling in IGF-1 has shown to extend the lives of a variety of species.
- Those born with genetically lower IGF-1 levels are more more likely to live to be nonagenarians.
- Each year you destroy and create nearly your entire body weight in cells. 50 billion of your cells die and are reborn everyday. During infancy or puberty, your cells don't grow in size as you mature, they grow in number. As an adult, you may have around 40 trillion cells.
- IGF-1 is a key hormone for regulating cell growth. Higher IGF-1 levels correlate to higher risk of developing some cancers.
- As you age, your risk of developing and dying from cancer grows every year - until you hit 85 or 90. Then your cancer risk begins to drop. Centenarians appear 10 times less likely to die from malignant tumours than people in their 50s and 60s.
- Association between milk consumption and IGF-1 levels have a very small P-value.
- Animal protein increases levels of IGF-1 but not plant protein. This is because animal proteins are structurally similar to human proteins. Animal proteins are like prefabricated, easy-to-use building blocks that quickly trigger growth (higher IGF-1), while plant proteins require more effort to process, leading to a slower, more controlled response.
- To help reduce IGF-1:
- Stick with 0.8g per healthy kg of body weight, about 55g a day for the average height man
Inflammation
- For most of our time on Earth, infections were the leading cause of death and disease. We evolved to have a high alert immune system, erring on the side of overreaction rather than under-reaction.
- Inflammation is your body's natural reaction to tissue damage or irritation. Its purpose is to trigger the healing process. Chronic inflammation, or metabolic inflammation (meta-inflammation) can be picked up on blood tests showing high levels of C-reactive protein (CRP).
- CRP levels rise as we age and are associated with reduced survival. Having higher CRP levels may increase your risk of dying prematurely. Interleukin 6 (IL-6), the most important trigger for CRP production, may be a better predictor. Interleukins are chemical messengers used to communicate between white blood cells (inter - between, leukocytes - white blood cells).
- Visceral fat can spill out inflammatory factors.
- The most pro-inflammatory foods are saturated fat and trans fat.
- Endotoxins are highly pro-inflammatory structural components of certain types of bacteria. As such, the highest levels of these endotoxins are found in foods with high bacterial loads, like meat.
- Lowest levels of endotoxins are found in whole fruits and vegetables. Endotoxins can build up in refrigerated pre-chopped vegetables.
- Not all high-fat foods cause inflammation. For example, nuts don't increase inflammatory markers, nor does avocados.
- Excess sodium raises not only your blood pressure but also the level of inflammation in your body.
- The most anti-inflammatory food is turmeric, ginger, and garlic. Green tea or black is the most anti-inflammatory beverage. The most anti-inflammatory food components are fibre and flavones. Dietary fibre is mostly concentrated in whole grains and legumes, such as chickpeas, beans, lentils, and split peas. Flavones are concentrated in fruits, herbs, and vegetables.
- Interleukin 10 (IL-10) may be the most potent anti-inflammatory cellular messenger in our blood. Eating more fibre boosts IL-10.
- Common berries can reduce markers of inflammation. The bioflavonoids in citrus can help with muscle fatigue during workout, but the anthocyanins in berries may help you deal with post-exercise inflammation.
- Cruciferous vegetables, which include kale, collard greens, and others in the broccoli family, may be anti-inflammatory.
- 3 servings of whole grains would lead to a 17% lower overall risk for mortality.
- To decrease inflammatory aging:
- Apply emollient skin lotion
- Avoid pro-inflammatory foods by minimising intake of meat, dairy, tropical oils, and salt
- Eating foods shown to be anti-inflammatory, such as legumes, berries, greens, tomato juice or paste, oats, flaxseeds, turmeric, ginger, garlic, cinnamon, cocoa powder, dill, green and chamomile teas
mTOR
- Bacteria in a vial of dirt taken from Easter Island was named rapamycin. Rapamycin inhibits an enzyme that came to be known as mTOR, or "mechanistic target of rapamycin." mTOR has been characterised as a "master determinant of lifespan and aging."
- mTOR is a major regulator of growth in animals. Since most animals die early and don't experience aging, the best evolutionary strategy was to run at full speed. However, after childhood, we are still going at full pace thanks in part to this enzyme.
- This is the trade-off theory of aging - antagonistic pleiotropy. Unconstrained, mTOR actively suppresses autophagy. Conversely, putting brakes on mTOR seems to slow down the aging process.
- Rapamycin worked for other animals but not ready for humans.
- Restricting protein, and amino acids from animal derived protein such as leucine may combat mTOR activation.
- Vegetables in the broccoli family cools down mTOR.
- To slow mTOR production:
- Follow steps to boost AMPK
- Stick with 0.8g per healthy kg of body weight, about 55g a day for the average height man
Oxidation
- The mitochondrial theory of aging suggest that, over time, free radical damage to our mitochondria leads to a loss of cellular function and energy.
- Free radicals are unstable and reactive molecules with an unpaired electron.
- We may be able to reduce our mitochondrial free radical production rate through exercise, as well as lowering the intake of methionine.
- Methionine content in tissues is linked with to maximum lifespan among mammals. Low methionine content in legumes have once been thought to be a disadvantage, but now it is advantageous since it is also consistent with the data showing legume consumption may be the most important dietary predictor of survival in older people around the world.
- Since humans have been evolving with our common great ape ancestor for 20 million years, our Paleolithic diets of 200,000 years is only a fraction of our formative years.
- Humans are the only mammals so adapted to a plant-based diet, if we don't enough we might die from scurvy. Most other animals produce their own vitamin C, but why would our bodies expend that energy when we evolved to eat fruits and vegetables all day long?
- Our prehistoric ancestors consumed a larger amount of antioxidants than we do but had less need for them. In modern life, we are surrounded by pro-oxidant stresses, air pollution, cigarette smoke, alcohol, junk food, pesticides, and industrial chemicals. Today, we are able to get fresh produce from all over the world, making it easier to have a steady intake of antioxidants in our diet.
- Pro-oxidative stresses, such as drinking green tea or exercise has been shown to increase the activities of our antioxidant enzymes. This concept that "what doesn't makes you stronger" notion is known as hormesis.
- Nrf2 is a protein that promotes antioxidant properties in cells. Sulforaphane, found in cruciferous vegetables promotes Nrf2 activity in cells and studies have shown it is a protective factor.
- Acidifying raw cruciferous vegetables, like adding vinegar can help boost sulforaphane production. After cutting cruciferous vegetables, waiting 40 minutes before cooking them will help sulforaphane production. Another method is adding mustard while cooking the vegetables.
- To slow the rate of free radical production and increase Nrf2 and radical resistance:
- Exercising
- Restricting methionine intake
- Activating Nrf2 defences by eating cruciferous vegetables and drinking green tea
- Eating berries and other vibrantly coloured foods
- Using herbs and spices, such as cinnamon, cloves, garlic, ginger, and marjoram
Sirtuins
- Each of us have 10 billion miles of DNA. How does our body prevent these ribbons from being twisted and tangled? Enzymes known as sirtuins keep our DNA neatly wrapped and silence whatever genes are in that stretch of DNA.
- Sirtuins may have longevity properties in humans.
- Health benefits of resveratol, the molecule in red wine has been debunked. It was previously thought to have increased sirtuin activity, but comes with safety concerns.
- Apples have been shown to increase sirtuin levels, as well as APMK and autophagy, while suppressing mTOR signalling. Meta-analysis of population studies show that people who eat more apples have a 15% lower risk of premature death.
- Cardamom has been shown to increase sirtuin levels.
- To increase sirtuin levels:
- Elevate NAD+ levels
- Follow AMPK activation
- Snack on apples and add cardamom to meals
Telomeres
- Telomeres are analogous to plastic tips at the end of our shoelaces, they stop DNA from unraveling. Each time a cell divides, a bit of the telomere is lost.
- Large scale studies showed that longer telomeres meant a longer life.
- Looking "old for your age" is actually an indicator of poor health.
- Telomerase was found in a tree named Methuselah. It is an enzyme that rebuilds telomeres.
- Studies show that the diet, not exercise or how much weight determined, acquired telomere protection.
- Refined carbs, alcohol, and saturated fats showed telomere loss.
- Omega-3 fats found in fish and fish oil showed no evidence of affecting telomere length.
- Green tea, coffee, and cruciferous vegetables helped boost telomere length.
- Vitamin D supplements (800 IU a day) showed benefits in telomeres.
- To boost telomere length:
- Eat a high fibre diet around whole plant foods
- Choosing tea and coffee over soda
- Eating cruciferous vegetables
- Supplementing with 800-2000 IU of Vitamin D3 a day
Conclusion
- A boost in AMPK downregulates mTOR while upregulating autophagy and NAD+ levels, which raise the sirtuin activity that then lowers IGF-1 and feeds back on AMPK.
The Optimal Anti-Aging Regimen
Diet
- According to the Global Burden of Disease Study, the most comprehensive and systemic analysis undertaken on the causes of death, conclude that the number 1 killer in the world is a bad diet.
- The diets that had been shown to extend lifespan, lower heart disease, and cancer mortality shared 4 fundamental elements: more fruits, more vegetables, more whole grains, more nuts and beans.
- What does the phrase "best available balance of evidence" mean? A single study may not be helpful as a compilation of studies, a single review may not be helpful as a compilation of reviews. Looking at review of reviews, the vast majority show that whole plant foods are protective and animal-based foods as deleterious.
- The omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA present in fish oil fats had no effect on cardiovascular health. Only plant-based sources such as flaxseeds and walnuts might be protective. However, these omega-3s are important for brain health, and there are algae based sources of EPA and DHA.
- 9/10 reviews show that whole plant foods are, in the very least, not bad, whereas 8/10 reviews show that animal products are not good.
- Processed meat is classified as a group 1 carcinogen by the most prestigious cancer research institution in the world.
- The benefits of plant-based eating likely comes from the dual action of increasing protective dietary factors like fibre while decreasing intake of pathogenic dietary factors like saturated fat.
- We started using tools in the Paleolithic period (2 million years ago) but we and other great apes have been evolving from 20 million years ago. Our body evolved on mostly plants for 90% of our hominoid existence.
- For most of human existence, we only got a pinch of salt that's naturally found in whole foods. Today, due to processed foods, we're exposed to 10 times more than our bodies can handle.
- Don't cook with salt or add it to food. It may taste bland, but in 2-4 weeks salt-taste receptors in your mouth become more sensitive so the flavour of your food improves. Play around with pepper, lime, onions, basil, garlic, tomatoes, thyme, sweet peppers, parsley, chilli powder, celery, lemon, rosemary, smoked paprika, curry, and coriander.
- The American Heart Association's recommended limit is 1500 mg of sodium a day. We also would have evolved to have 10,000 mg of dietary potassium a day (potassium lowers blood pressure.)
- Longevity experts consider nutrition to be the most important intervention for the promotion of health and prevention of the great majority of chronic diseases. The largest lifespan gains would be made by eating more legumes, then whole grains and nuts, and cutting down sugary beverages.
Beverages
- How much water should you drink? If your pee is pale gold or the colour of straw, then you're hydrated. A darker yellow, amber, or brownish has been a validated way of detecting dehydration.
- The World Health Orginisation and US Institute of Medicine recommend daily 8-11 cups of water for women and 10-15 cups for men. We get around 4 from food and burning fat, so 4-7 cups for women and 6-11 cups for men.
- A review of 96 meta-analyses of observational studies showed increasing tea consumption by 3 cups a day may decrease the risk of premature death from all causes by 24% - equivalent to adding 2 years to your lifespan. This applies to both green and black tea.
- Rooibos or redbush tea has been shown to have antioxidant properties.
- Mendelian randomisation (MR) is a method used in epidemiology and genetics to assess causal relationships between risk factors and health outcomes. It leverages genetic variants that are randomly inherited at conception, mimicking a randomised controlled trial.
- MR studies showed that lower alcohol consumption led to a lower risk of heart disease.
What Do Centenarians Eat?
- There are 5 authenticated "blue zones" in the world - longevity hotspots. They are the Nicoya Peninsula in Cost Rica, the island of Sardinia in Italy, Ikaria in Greece, Okinawa in Japan, and Loma Linda, California. These are the regions with high concentrations of centenarians.
- They share a number of characteristics, such as low smoking rates, daily moderate physical activity, social engagement, and diet around whole plant foods.
- Researchers found of all the foods considered, the largest lifespan gains would be expected from eating more legumes.
- Randomised control trials show that eating legumes reduces cardiovascular risk factors.
- A faster resting heart rate may lead to a faster death rate. Men with 90 bpm had a higher risk of sudden cardiac death than compared to those in the safety zone of 60 bpm.
- In studies on spicy food and mortality found that a significant decrease in death risk from people who ate more spicy chilies.
The Mediterranean Diet
- The main characteristic of a Mediterranean diet is that it's mostly plant-based, which explained the low rates of coronary heart disease.
- Olive oil, contrary to common knowledge, can still impair arterial function. As well as palm oil, soybean oil, and sunflower oil. This does not happen with Green Light sources of fat, like nuts or avocados.
- The PREDIMED study showed that those consuming a greater amount of nuts had a significantly lower overall risk of dying prematurely.
The Okinawan Diet
- The Okinawan diet revolved around steaming sweet potatoes, leafy greens and other vegetables, and soy, in the form of tofu or miso soup.
- Sweet potatoes is rated the single highest nutrient-rich food score per dollar. Anthocyanins are a class of natural purple, red, and blue pigments found in berries, grapes, plums, red cabbage, and red onions. Purple sweet potatoes were found to have the most antioxidant activity.
- High intake of isoflavones, the natural phytoestrogens in soy, were associated with a lower risk of premature death.
- Miso is not associated with stomach cancer risk attributed to other fermented foods, like kimchi, nor the risk of developing high blood pressure.
- Seaweed consumption was associated with lower blood pressure and may boost your immune function. They are a good source of iodine, which you can consume intermittently.
- Ergothioneine, found in mushrooms and tempeh, was associated with lower rates of disease and death. In terms of ergothioneine content in mushrooms, porcinis>oyster and shiitake>white, cremini, portobello.
- Garlic, ginger, and tumeric have all been shown to improve health outcomes.
Plant-Based Eating
- The Seventh Day Adventists in Loma Linda live longer than the average population, due to their plant based diet.
- A whole foods plant based diet consists of maximising intake of whole plant foods, such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes (beans, split peas, chickpeas, and lentils), mushrooms, nuts and seeds, herbs and spices.
- Vegan diet does not necessary mean health promoting, vegan junk food is still junk food.
- Vegans and vegetarians should supplement 50 mcg of cyanocobalamin per day, or 2000 mcg once per week.
- We produce our own vitamin K2 from K1 which is present in greens.
Lifestyle
- Adhering to 4 simple lifestyle choices can have strong impact on the prevention of our deadly diseases: not smoking, not being obese, getting 30 minutes of exercise per day, and eating more healthfully.
Exercise
- Population studies have found a link between aerobic exercise and decreased risk of disease.
- It may be recommended to limit chronic, vigorous exercise to 1 hour a day, 5 days a week with 2 days off. For runners, the upper recommended limit for longevity benefits is no more than 50kms a week.
Weight Control
- The largest studies show that having a BMI of 20-22 is optimal.
Sleep
- Scientists showed that individuals in pre-industrial societies, isolated from each other by continents, got around 7 hours of sleep a night.
Preserving Function
Dr. Greger's Anti-Aging Eight
Introduction
- Anti-aging quackery has been around forever, but has increased recently due to the rise in aging baby boomers, online availability and advertising, and the passage of the 1994 Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA).
- The DSHEA removed quality control, safety, and efficacy for supplement manufacturers.
- Randomised control trials of multivitamins have shown to have no overall benefit to mortality.
- Vitamin D have shown to have some benefits, but should not be heralded as the cure-all.
Nuts
- Randomised control trials have shown nuts can improve the risk factors for our leading killers.
- How many nuts should we eat per day? Around 20g a day - 9 hazelnuts, 10 walnut halves, 13 cashews, 17 almonds, or 25 peanuts.
- The healthiest nut would probably be walnuts for their artery function improvement.
Greens
- Broccoli and other cruciferous vegetables protects us against pathogens in food and also pollutants found in the environment.
- Nitrates found in leafy green vegetables improves the efficiency of our mitochondria. The 10 most common food sources of nitrates are:
- Arugula (Rocket)
- Rhubarb
- Cilantro/Coriander
- Butter lettuce
- Spring greens
- Basil
- Beet greens
- Oak leaf lettuce
- Swiss chard
- Beets
- Nitrates can improve exercise tolerance and performance since it enables our body to extract more energy from oxygen and dilates our arteries so they can deliver more oxygenated blood to our muscles.
- The healthiest way to get your nitrates is to eat a big salad everyday.
- Nitrate activation step happens in your mouth thanks to the good bacteria in your tongue. Foster the growth of nitrate-metabolising bugs by eating nitrate-rich vegetables regularly, don't use antiseptic mouthwash, and clean your tongue daily.
Berries
- Greens are the healthiest vegetables and berries are the healthiest fruits.
- Berries have the highest antioxidant power out of all fruits.
- Goji berries are better than raisins.
Xenohormesis and microRNA Manipulation
- Hormesis is the "what doesn't kill you makes you stronger" principle. Physical activity is a strong example.
- Plants have evolved to produce compounds and antioxidants to fight bacterias and heal wounds.
- Xenohormesis explains how environmentally stressed plants produce bioactive compounds that can confer survival benefits to those that consume them. Drought-stressed strawberries for example, have more antioxidants and phytonutrients.
- Levels of phytonutrients are higher in organic vegetables than conventionally grown ones.
- Sulforaphane is produced by plants to dissuade nibblers with bitterness.
- microRNAs are 20 letters long code that prevent RNAs from being translated into proteins.
- If DNA is the blueprint and RNAs are the construction workers translating those instructions into a house, microRNAs are like building inspectors who intercede and keep particular workers from carrying out their duty.
Prebiotics and Postbiotics
- Centenarians from different parts of the world have microbiomes in common, particularly from eating high fibre diets.
- Salt and artificial sweeteners can ruin your microbiome.
- Systemic review of randomised control trials of probiotic supplements show insufficient evidence of improvement of health outcomes.
- Fibre in plant foods is the best prebiotic, probiotic, and postbiotic.
Caloric Restriction
- 3 meals a day plus snacks is an evolutionary novel behaviour. Most of our evolutionary history on Earth has been of starvation.
- The CALERIE (Comprehensive Assessment of Long-Term Effects of Reducing Intake Energy) was the first large, long-term, clinical trial to test the effects of caloric restriction. It showed that just a small restriction in calories led to positive quality of life benefits.
- Alternate day fasting have been shown to have no benefits, at most it increases LDL cholesterol.
- Shifting food intake toward the morning has shown to be beneficial.
Protein Restriction
- A new hormone was discovered in 2000, the 21st fibroblast growth factor named FGF21. Exercise and protein restriction increases FGF21 levels.
NAD+
- Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is an essential molecule present in all living organisms, required for many enzymatic reactions.
Conclusion
- Diet is understood as the number one determinant of how long we live.
- From 20 million years ago until we split from our last common primate around 2 million years ago, we ate what the other great apes were eating, a diet around whole plant foods. Even the most carnivorous of apes - chimpanzees - eat a diet that is 98% plant based.
- Research from Pritikin, Ornish, and Esselstyn showed plant-based diets can reverse heart disease.
